Quitting smoking after cancer diagnosis improves survival across a wide variety of cancers
Smokers who are diagnosed with cancer now have more incentive to quit, as researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have found survival outcomes were optimized when patients quit smoking within six months of their diagnosis.
Study results, published today in JAMA Oncology, found a 22%-26% reduction in cancer-related mortality among those who had quit smoking within three months after tobacco treatment...

Dual immunotherapy plus chemotherapy benefits specific subset of patients with lung cancer
Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have demonstrated that patients with metastatic non-squamous non-small...
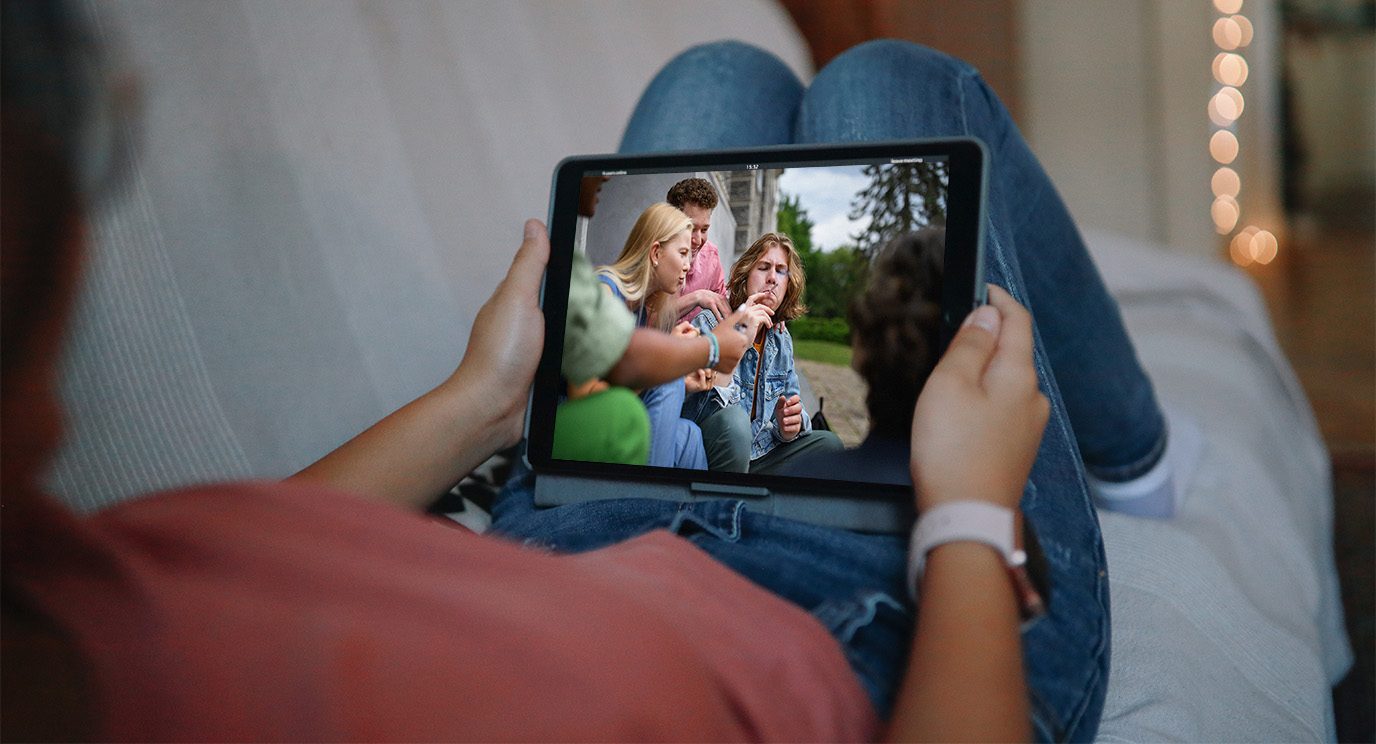
Americans face disparities in exposure to tobacco on streaming platforms
Tens of millions of Americans are being exposed to tobacco content on streaming services, according to new research from The University of...
Pre- and post-surgical immunotherapy improves outcomes for patients with operable lung cancer
Compared with pre-surgical (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy alone, adding perioperative immunotherapy – given before and after surgery – significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) in patients with resectable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from the Phase III CheckMate 77T study were published today in the New England Journal...
Increasing doses of varenicline or nicotine replacement helps persistent smokers quit
For most smokers, quitting on the first attempt is likely to be unsuccessful, but a new study from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer...
Cancer screening rates are significantly lower in U.S. Federally Qualified Health Centers
A national study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and The University of New Mexico (UNM) Comprehensive...
Biomarker-directed combination effective in immunotherapy-resistant lung cancer
A specific combination of targeted therapy and immunotherapy may better help patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) overcome inherent...
Cervical cancer rates rising in low-income U.S. counties
Women in low-income areas of the U.S. face a stark rise in cervical cancer incidence and mortality, according to a new study led by researchers...
ASH: Targeted oral therapy reduced disease burden and improved symptoms for patients with rare blood disorder
ABSTRACT: 77
The targeted therapy bezuclastinib was safe and rapidly reduced markers of disease burden while also improving symptoms...
Eating beans improves gut health, regulates immune and inflammatory processes in colorectal cancer survivors
Incorporating navy beans into the diet of colorectal cancer (CRC) survivors has the potential to positively impact both gut and host health...