request an appointment online.
- Diagnosis & Treatment
- Cancer Types
- Lung Cancer
Get details about our clinical trials that are currently enrolling patients.
View Clinical TrialsLung cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the tissues of the lungs, most often in the cells that line air passages. It occurs when these cells start to grow and multiply uncontrollably, usually as a result of exposure to toxins such as tobacco smoke, radiation and asbestos.
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the tissues of the lungs, most often in the cells that line air passages. It occurs when these cells start to grow and multiply uncontrollably, usually as a result of exposure to toxins such as tobacco smoke, radiation and asbestos.
Symptoms
Lung cancer symptoms vary from person to person. Some people with lung cancer don't have any symptoms. Often, symptoms are easily confused with common respiratory illnesses such as bronchitis or pneumonia, delaying an accurate diagnosis.
The most common symptoms of lung cancer include:
- Cough that does not go away and gets worse over time
- Chest pain that is constant and often made worse by deep breathing, coughing or laughing
- Arm or shoulder pain
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored phlegm
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Hoarseness
- Infections like pneumonia or bronchitis that do not go away or come back often
- Swelling of the neck and face
- Loss of appetite and/or weight loss
- Feeling weak or tired
- Widening of the fingertips and nailbed also known as “clubbing"
If lung cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it may cause:
- Bone pain
- Arm or leg weakness or numbness
- Headache, dizziness or seizure
- Balance problems or an unsteady gait
- Jaundice (yellow coloring) of skin and eyes
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or shoulder
These symptoms do not always mean you have lung cancer. However, it is important to discuss any lung cancer symptoms with your doctor, since they may also signal other health problems.
In rare cases, lung cancer can be passed down from one generation to the next. Genetic counseling may be right for you. Visit our genetic testing page to learn more.
Molecular diagnosis
Lung cancer traditionally is categorized by the type of cell where it begins. Today, doctors can also diagnose the disease on a molecular level.
This approach usually looks for mutations in the DNA of cancer cells and/or proteins produced by the cells. There are hundreds of different molecular diagnoses, including mutations to the EGFR, ALK, KRAS and ROS1 genes.
These molecular subtypes can impact how quickly the disease grows and spreads. They also can predict how the disease will respond to specific treatments, including different types of chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy. By diagnosing a patient’s disease on a molecular level, doctors can design treatment plans with the best chance of fighting each patient’s specific cancer.
Cellular diagnosis
The traditional diagnosis based on the type of cell where the cancer started can still help doctors understand the patient’s condition and make a treatment plan. The two main categories are:
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
About 85% of lung cancer cases are considered NSCLC. It arises from the lungs’ epithelial cells, a type of cell that lines the surface of organs. There are several types of non-small cell lung cancer based on the type of epithelial cell where the disease begins, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
About 15% of lung cancers are SCLC and almost always are caused by smoking tobacco. It often starts in the more central portions of the chest. It usually grows and spreads quickly to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes. Because it is so aggressive, surgery is used less often for small cell lung cancer than non-small cell lung cancer.
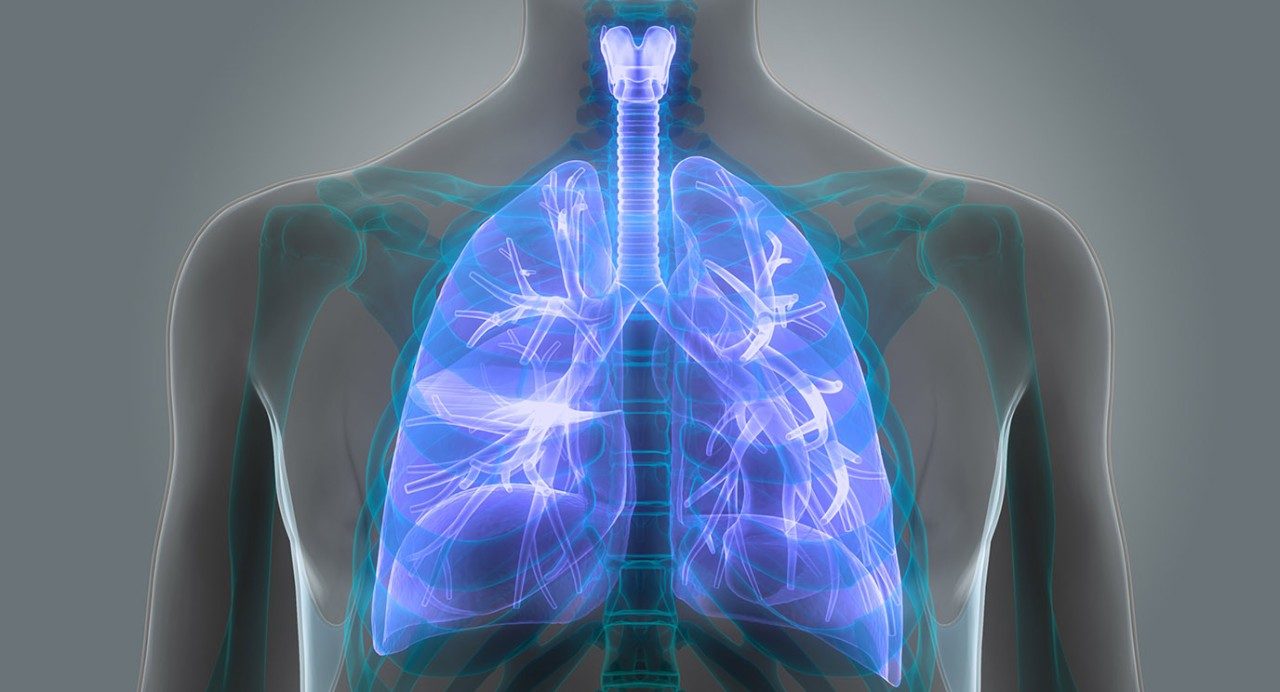
Lung anatomy
When you breathe in, oxygen comes through your mouth and nose and then travels through the trachea, or windpipe. The trachea divides into two tubes called bronchi, which take the oxygen to the left and right lungs. Inside the lungs are smaller branches called bronchioles and alveoli, tiny air sacks where oxygen is transferred to the blood stream.
Each lung is divided into sections called lobes. The right lung has three lobes and the left lung has two lobes. The left lung is smaller than the right lung because the heart is also located in the left side of the chest. Each lobe can be further divided into bronchopulmonary segments.
The pleura is a thin membrane that covers the outside of each lung and lines the inside wall of the chest. The space between the lungs and the chest wall usually contains a very small amount of fluid that allows the lungs to move smoothly during breathing.
Cancer grows in lungs, may spread
When lung cancer is small and at an early stage, it usually does not cause symptoms. However, once the disease grows, it may damage surrounding tissue, interfering with the lungs’ normal function and causing symptoms such as hemoptysis (coughing up blood), shortness of breath or pain.
Lung cancer frequently spreads, or metastasizes through the lymphatic system. Lymph is a clear fluid that is drained from our tissues and contains immune cells that help fight infection. It travels through your body in lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs that link lymph vessels. They often trap cancer cells that have spread to the lymphatic system.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of your body through the bloodstream, as well. When lung cancer spreads to other organs such as the liver or bone, it is known as stage IV lung cancer or metastatic lung cancer. Cancer that has spread to another organ is still referred to as lung cancer. Whether or not a lung cancer has spread to lymph nodes or to other organs significantly influences how the tumor is treated.
Lung metastases
Sometimes, a tumor starts in another part of the body and then spreads, or metastasizes, to the lungs. These tumors are called lung metastases, and they are not the same as lung cancer. In these cases, they are the type of cancer where they came from. For example, a colon cancer with lung metastases is called metastatic colon cancer.
Statistics
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer-related deaths and second most common cancer in both men and women in the United States. According to the National Cancer Institute, more than 230,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with the disease each year. While most cases are linked to tobacco smoking, a growing number of diagnoses are among non-smokers, especially among women. Most lung cancers are diagnosed after the disease has spread. As a result, the five-year survival rate for lung cancers is 22%, though cases that are caught before the disease has spread have a much higher survival rate.
Risk factors
A risk factor is anything that increases the chance that a person will develop a particular disease. The main risk factors for lung cancer are:
- A history of or current tobacco use
- Exposure to second-hand smoke
- Exposure to asbestos, arsenic, chromium or other chemicals
- Living in an area with air pollution
- A family history of lung cancer
- Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Radiation exposure, including radiation therapy to the breast or chest, and radon exposure. This is a minor risk factor and the benefits of radiation therapy as a cancer treatment far outweigh the risks.
In some cases, lung cancer can be passed down from one generation to the next. Genetic counseling may be right for you. Visit our family history site to learn more about genetic counseling and testing.
Learn more about lung cancer:
- Lung cancer symptoms
- Lung cancer diagnosis
- Lung cancer stages
- Lung cancer treatment
- Lung cancer research
Learn about clinical trials for lung cancer.
MD Anderson is #1 in Cancer Care
Podcast: Lung cancer research and clinical trials
What's the best way to quit smoking?
Smoking is on the decline. But if you are one of the 28 million Americans still smoking, you probably know how hard it is to quit.
Close to 70% of smokers report that they want to stop smoking. Of those, 53% said they tried to quit in the previous year. Only around 9% succeeded.
There are plenty of reasons to try to reduce your nicotine addiction: Tobacco use – and smoking, in particular – accounts for about one-third of all cancers, and up to 90% of lung cancer cases. It also contributes to heart disease, stroke and lung disease.
So, what's the best way to quit smoking?
“The best way to quit smoking is with a combination of medication and counseling,” says Maher Karam-Hage, M.D., medical director of the Tobacco Research and Treatment Program at MD Anderson. “They both help. But you double your chances by using both compared with one of them.”
What products can help you quit smoking?
There are several products that can help reduce your nicotine cravings.
Prescription medication
Smoking cessation options that require a doctor’s prescription include:
Varenicline (formerly sold as Chantix) works in two ways. First, it provides a mild version of nicotine’s effects. This helps reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Second, it stops your brain from feeling the pleasurable effects of nicotine when you smoke. This makes smoking less appealing. Varenicline is the most effective single medication, Karam-Hage says. But it's also the most expensive.
Bupropion (also sold as Zyban or Wellbutrin) blocks the effects of nicotine in your brain. This makes smoking feel less pleasurable, but it does not replace the effect of nicotine.
Nicotine nasal spray is a nicotine replacement therapy that is sprayed into the nostril and absorbed into the nasal lining and bloodstream. This product provides nicotine without the other harmful effects of cigarettes.
Over-the-counter options
Over-the-counter nicotine replacement therapies partially satisfy nicotine cravings by giving the body small amounts of nicotine. This can help with cravings and make it easier to stop smoking.
The over-the-counter nicotine replacement therapies available in the United States are:
Nicotine patches are 3- or 4-inch-wide patches that release a steady dose of nicotine. They are applied to the upper body and changed daily. They come in 7 mg, 14 mg and 21 mg doses.
Lozenges release nicotine as they dissolve in the mouth. They are available in mini and regular sizes and 2 mg and 4 mg doses.
Nicotine gum users follow the ‘chew and park’ method. The gum is chewed for 5 to 10 seconds then parked between the teeth and cheek for another 5 to 10 seconds. This process is then repeated in different parts of the mouth. It comes in 2mg and 4 mg doses.
Why is counseling important?
Working with a counselor can help you better understand your medication. A counselor can also give you the tools to cope with setbacks, stress and cravings by building skills in several areas. These include:
Problem solving
We all run into problems in life, like personal conflicts, that can make us feel helpless. Working with a counselor to tackle them one at a time can help you build knowledge and skills that can be used in other areas.
Coping strategies
Anything from a traffic jam to a death in the family can set off a strong urge to smoke. Learning strategies like deep breathing exercises, meditation and mindfulness can help a smoker get to the other side of a crisis without smoking.
Behavior change
Smokers who quit may miss the “hand-to-mouth” act of smoking. Counseling can help them find substitutions like using a straw, cinnamon stick or gum.
Identifying triggers
Counseling can help you identify what triggers you to smoke, like that morning cup of coffee or spending time with friends who smoke. Once you identify your triggers, you can learn to deal with them or avoid them.
Once smokers start counseling, they appreciate the tools and support it provides in their effort to quit smoking, Karam-Hage says.
“Finally, somebody understands the struggle they're going through,” he says. “Someone is acknowledging that it's not a simple thing to quit. That is very helpful.”
What option should you try first?
Not sure where to start? For many, over-the-counter nicotine replacement therapies are quicker and easier to get than medication because they don’t require prescriptions and can be purchased at most pharmacies.
However, remember that nicotine replacement therapies must be used consistently to be effective. If you find it hard to regularly use options like the patch, lozenges or gum, or if they don’t help you quit, Karam-Hage says you might consider medication.
Your doctor can prescribe medication to help you quit. They can also advise you on how to combine nicotine replacement therapies. This might look like using the patch along with either nicotine gum, lozenges or nicotine nasal spray.
Additionally, a professional counselor can help you monitor what is and isn’t working and work with a prescriber on your care team to adjust the medication you take to set you up for success.
Want to quit but don't have access to a comprehensive program that includes both counseling and medication? You have options.
You can get phone and text support through the National Institutes of Health Quitline by calling 1-800-784-8669, texting QUIT to 47848, or visiting SmokeFree.gov. If you live in Texas, you can use the Texas Tobacco Quitline by calling 1-877-YES-QUIT or visiting YESQUIT.org.
Should you quit smoking cold turkey?
Knowing the health risks and addictive properties of nicotine, you might be wondering whether you should simply quit smoking cold turkey.
Karam-Hage says it’s wonderful if a smoker can quit cold turkey, but notes it is not necessarily better than using medication and counseling. This is because while it works for some, it does not work for everyone.
Most people who attempt to quit smoking on their own fail to do so, he says. Because of this, he notes people may benefit from using both medication and counseling in future attempts to quit smoking. He says the unfortunate reality is that only about 30% of people attempting to quit get either medication or counseling, and only 5% of people get both medication and counseling.
If you’ve tried and failed to quit smoking long-term, Karam-Hage recommends a combination of counseling and medication. Enrolling in a comprehensive tobacco treatment program like MD Anderson’s Tobacco Research and Treatment Program, which is open to MD Anderson patients and caregivers, can be helpful for those seeking additional support. A 2019 study showed that 45% of people enrolled in MD Anderson’s program managed to quit smoking.
What happens to your body when you quit smoking?
Let’s start with the organ that is perhaps most associated with smoking: the lungs.
Those who quit smoking might note that they can breathe a little easier – and not just metaphorically! Karam-Hage says this is because the toxins from cigarette smoke are gone.
As for whether the lungs can regenerate after you quit smoking, the answer depends on just how damaged the lung tissue is. For lung tissue that is damaged but still alive, Karam-Hage says it is possible for it to recover. However, totally damaged cells can’t be reversed.
“Whatever cells have died are gone and no regeneration is possible,” he says, noting this is why conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are permanent.
While smoking’s effects don’t entirely go away when you quit, Karam-Hage says there are many positive health impacts that happen when you quit smoking.
These benefits include:
- Reduced heart rate and blood pressure
- Reduced level of carbon monoxide in blood
- Improved circulation and lung function
- Improved sense of taste and smell
- Reduced risk of heart disease
- Reduced risk of stroke
- Reduced risk of mouth, throat, larynx, esophageal, bladder, cervical, lung, kidney, liver, colorectal, leukemia and pancreatic cancer
“There are many benefits, and they continue to get better as time passes,” he says.
Request an appointment at MD Anderson online or call 1-877-632-6789.
Lung nodules (pulmonary nodules): What you need to know
Lung nodules — or pulmonary nodules — are small growths that can develop in the lungs. By definition, they are no larger than 3 cm, or about 1.25” across. Anything bigger than that is considered a mass.
Lung nodules are very common. But most lung nodules are not due to cancer.
So, why do lung nodules even form? Do they ever cause any symptoms? And, what should you do if you find out you have one?
Read on to learn the answers to these and other questions about lung nodules.
How serious is a lung nodule?
The answer to that question depends on the answer to several others.
- Number: Is there only one, or are there many lung nodules?
- Size: How big is it/are they?
- Age: How old are you?
- Family history: Does any type of cancer run in your family?
- Medical history: Have you ever had a lung infection?
- Work history: Have you ever been exposed to asbestos or radon?
- Social history: Have you ever smoked, vaped or used other tobacco products?
The older you get, the more common benign — on non-cancerous — lung nodules become, particularly if you live in certain parts of North America. But it’s more concerning if you have many nodules and have had cancer before than if you only have one and have never had cancer.
Anything larger than a green pea (about 5 mm) is worth investigating, but even smaller nodules might call for monitoring. And, answering “yes” to any of the history-related questions above significantly raises the risk that a nodule might be cancerous.
Why do lung nodules even occur?
People may develop lung nodules for many reasons. These include:
- Old infections, which can cause scarring
- Chronic infections, such as tuberculosis
- Sarcoidosis and rheumatoid arthritis, both autoimmune disorders
- Prior trauma, such as a gunshot wound or auto accident
- Cysts, or hollow sacs filled with fluid
Congenital conditions
- Arterial venous malformation, which shows up as dark spots in the middle of lung
- Pulmonary sequestration, when a segment of lung has its own blood supply
- Congenital emphysema, which some babies are born with
Certain fungal infections
- Blastomycosis (Great Lakes area)
- Coccidiodomycosis or Valley Fever (San Joaquin Valley)
- Histoplasmosis (Mississippi Valley)
Lung nodules may also be cancerous. When that happens, they could either be caused by lung cancer or a different type of cancer that has spread to the lung from another place.
Unfortunately, the lung is a very common location for metastatic disease. That means many other cancers tend to spread there. Sarcomas, for instance, often spread to the lungs. So does colorectal cancer. But technically, any type of cancer can spread to the lungs.
How are lung nodules usually found?
There are four main ways:
- An X-ray taken for an unrelated reason, such as an auto accident
- Imaging related to a lung problem, such as a cough that won’t go away or pneumonia symptoms
- A lung cancer screening
- A health screening performed before an operation
A rapid CT scan of the heart called a calcium score test is done to assess coronary artery disease. Sometimes, it catches the edges of the lungs in its field of vision, revealing nodules. Abdominal CT scans can also sometimes catch nodules in the lower third of the lungs.
Do lung nodules ever go away on their own?
Yes, especially if they’re related to an infection. Not so with any of the other possible causes, though. Cancer, in particular, will not go away on its own.
Do lung nodules ever cause any symptoms?
Yes. Even if they’re benign, the nodules themselves or their underlying causes can cause some of the same symptoms as lung cancer, including:
- A nagging cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or pressure
- Persistent or recurrent upper respiratory infections
How can you tell if a lung nodule is cancerous?
If a nodule appears completely calcified on imaging, as if the whole thing has turned to stone, it is not cancer. If it has some flecks of calcium in it, it might be cancerous. But if there’s no calcium in a nodule at all, we’re always going to find that suspicious. Still, there are three approaches to learning more.
- Watch it: Also known as surveillance, this means we monitor a nodule over time to see if it grows bigger, gets smaller or just stays the same.
- Re-image it: We use advanced imaging techniques — such as PET scans and high-resolution CT scans — to take a closer look.
- Sample it: We can either stick a needle in the nodule or remove the whole thing surgically. Either way, we’ll get a piece of it so we can biopsy the tissue.
The only way to know for sure if something is cancer is to look at its cells under a microscope. But we have to balance the risk of biopsy with the risk of it being cancer. That’s why we usually take a wait-and-see approach if your risk is very low or there’s a clear reason for a nodule, such as a recent case of the flu.
On the other hand, if you have multiple nodules, smoke a pack a day and have a family history of lung cancer, we might go straight to biopsy, because all of those factors put you at higher risk of lung cancer.
The longer a nodule remains unchanged, the lower your risk of cancer is and the more justified continued observation is, rather than exposing you to the risk of a biopsy. If a nodule remains stable and doesn’t grow over two years or more, it is not a cancer.
How are lung nodules usually treated?
That depends on how many there are, what kind they are, and whether they are causing any problems. Even if a lung nodule is not cancerous, if it’s causing repeated infections or making breathing difficult, we’ll often remove it.
But lung cancers and those that originate in other locations are treated very differently. So, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer.
What is a lobectomy?
A lobectomy is the surgical removal of one of the five lobes — or main sections — of the lungs. It is the most common type of operation used to treat lung cancer, and it may be performed on patients with various stages of the disease.
But is a lobectomy considered major surgery? How long does it take to fully recover? And will you feel short of breath after having one?
Read on for the answers to these questions and more.
What is a lung lobe?
Think of your airway as an upside-down tree. The trachea, or windpipe, is the trunk. The first two branches leading off of it go to the left and right lungs. Branches further down lead to the upper, middle, and lower lobes on the right, and the upper and lower lobes on the left.
We have five lung lobes in all: two on the left side and three on the right. These lobes can be further subdivided into 19 smaller units called “segments.” A segmentectomy is the surgical removal of a segment rather than an entire lobe.
How long does it take to fully recover from a lobectomy?
That varies widely. It depends on many factors, including:
- Which surgical approach is being used
- Your overall health status
- How well the rest of your lung lobes are functioning
On average, you can expect to spend two to three nights in the hospital afterward and have several chest X-rays taken to monitor your progress.
A chest tube will be inserted at the time of the operation. It will be left in place to allow the lung to re-expand and drain any air or fluid that accumulates. The tube is usually removed within a day or two of surgery when the volume of fluid draining is minimal and there is no longer any air bubbling from it.
In some circumstances, you may be ready to leave the hospital before that happens. In those situations, you’d likely return to the clinic within a few days to have the tube taken out.
What will my life be like after a lobectomy? Will I always feel short of breath?
No. A lobectomy would not be performed if it would leave you unable to breathe adequately or feeling permanently short of breath.
That being said, you might feel slightly short of breath for the first few weeks after a lobectomy while your body adjusts to its new anatomy. You may also experience some discomfort when taking deep breaths, but that should improve over time.
You will be assessed for your lung function before a decision is made to perform lung surgery. We calculate your eligibility based on pre-operative lung function and what percentage of lung tissue would be removed.
Is a lobectomy considered major surgery?
Yes. Any lung surgery is considered major surgery.
Is a lobectomy considered a high-risk procedure?
No. We might describe certain tumors or patients as high-risk based on their anatomy or overall health status. But it’s a very common operation. Even in complex situations, risks can be reduced by going to an experienced center of excellence like MD Anderson, where thoracic surgeons do it every day.
What are the risks of a lobectomy?
The greatest risks associated with lung surgery are:
- Prolonged air leaks: when the lung continues to leak air for more than a few days after surgery, requiring ongoing management with a chest tube
- Pneumonia: an infection of the lungs, which can be treated with antibiotics
- Atrial fibrillation (A-fib): an abnormal heart rhythm seen in roughly 8-10% of lobectomy patients, which is treated with medications
Fortunately, most of these conditions are temporary. Air leaks, in particular, are usually self-limiting. Pneumonia can often be prevented, too, with deliberate coughing, deep breathing, and a lot of walking after surgery.
What’s the difference between a pneumonectomy and a lobectomy?
A pneumonectomy is the removal of an entire lung. A lobectomy is just the removal of part of it (a single lobe).
What’s the most important thing to know about lobectomies?
Lobectomies are the most commonly performed operation on the chest. So, it’s important to have yours done well. That’s why you should go to a place like MD Anderson, where surgeons perform these procedures all the time.
Mara Antonoff, M.D., is a thoracic surgeon who specializes in the treatment of lung cancer.
Request an appointment at MD Anderson online or call 1-877-632-6789.
Bronchoscopy 101: How it helps diagnose and treat lung conditions
A bronchoscopy is a minimally invasive medical procedure in which doctors use a special scope to examine the inside of your lungs and airways. It is used frequently to diagnose and stage lung cancer.
But can a bronchoscopy tell us anything else? Do you have to be put to sleep to have one? And how long does it take to recover?
Read on, for answers to these questions and more.
What are the different types of bronchoscopy?
Diagnostic bronchoscopy
We use robotic bronchoscopy to biopsy lung nodules and a technique called endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) to sample lymph nodes for cancer staging.
We also use a technique called bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), typically in immunocompromised patients, to diagnose opportunistic infections of the lungs. To do a bronchoalveolar lavage, we wedge the bronchoscope in the section of the lung we’re interested in, flush it with a saline solution, extract the fluid, and culture it in a lab to see what grows.
Therapeutic bronchoscopy
Mostly performed via rigid bronchoscopy, this procedure is used to remove tumors that are blocking the windpipe, to cauterize bleeding tumors, or to place stents that keep the windpipe open. It won’t cure cancer, but it should make breathing easier.
How long does a bronchoscopy take?
That depends. The shortest procedure is the bronchoalveolar lavage, which can take just 10 to 20 minutes. The diagnostic bronchoscopy of a lung nodule can take 45 minutes to an hour, and the sampling of lymph nodes for staging can add another 45 minutes.
But if we’re doing it strictly for therapeutic purposes, it can take from one to two hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
Keep in mind, though, that these are all estimates. The length of each procedure is determined by the number of lung nodules or lymph nodes being biopsied, and doctors don’t know this until they are looking inside your lungs.
Are you awake during a bronchoscopy?
Not necessarily. You’ll be given general anesthesia in most cases, but moderate sedation if you only need bronchoalveolar lavage.
Is a bronchoscopy considered a serious procedure?
That depends on how you define it. I consider anything requiring general anesthesia to be a serious procedure.
But doctors will be working inside your lungs, which are the most vital organs aside from the heart. So, it is more serious than a colonoscopy, for example, but less serious than most surgeries.
Is a bronchoscopy considered a high-risk procedure?
Bronchoscopy for the diagnosis of lung nodules, sampling of lymph nodes, or bronchoalveolar lavage is commonly considered a moderate-risk procedure. On the other hand, therapeutic bronchoscopy is always considered high-risk because patients are sicker to begin with. They often have collapsed or obstructed airways, low oxygen levels, or they are actively bleeding.
What are the risks of a bronchoscopy?
With diagnostic and staging bronchoscopies, the risks are mainly from the anesthesia, rather than the procedure itself. General anesthesia can lower your blood pressure, which can be risky if you have underlying cardiovascular disease. It can also weaken the breathing muscles, so you tend to take shallower breaths when you wake up from anesthesia, and that can make your blood oxygen levels drop.
Biopsies of the lung nodules or lymph nodes have minimal risk of bleeding and infection, but biopsy of lung nodules can sometimes lead to lung collapse (pneumothorax). That’s why even if everything goes well, we prefer our patients to avoid long-distance traveling or air travel until the next day.
With therapeutic bronchoscopies, the risks are higher, and they generally involve bleeding, having low oxygen levels, and difficulty breathing. But all of these are dependent on each patient’s particular situation, and your doctor will go over which ones apply to you in detail.
How long does it take to recover from a bronchoscopy?
Most diagnostic and staging bronchoscopies are outpatient procedures. Patients remain in the recovery area for 45 minutes to an hour afterward, and then they go home. They generally feel tired on the day of their bronchoscopy, but they are back to their baseline the following day.
The recovery time is similar for therapeutic bronchoscopy patients, even if they are already admitted to the hospital.
Is a bronchoscopy painful?
No. The lungs have no pain receptors, so they do not hurt, and you are also sedated. You should not experience chest pain after bronchoscopy, either, unless you are coughing really hard.
Does a bronchoscopy have any side effects?
Some patients report having a sore throat due to the breathing tube. And patients can expect to cough up mucus tinged with blood for the next 2 or 3 days. But those are both normal and will resolve on their own.
Is a bronchoscopy better than a CT scan?
These two tests play very different roles. A CT scan is the test that generally finds out there is something wrong in your lungs. But it can only tell you that there’s an abnormality present. It cannot tell you exactly what it is. A CT scan is just the beginning.
For an accurate diagnosis, we have to examine tissue under a microscope. A bronchoscopy allows us to obtain that sample and make a diagnosis. If it turns out to be lung cancer, the tissue we obtain through a bronchoscopy can also be used for molecular profiling, so we can tailor your treatment to any specific genetic mutations. And bronchoscopy can, in addition, sample the lymph nodes to determine the stage of lung cancer.
Can a bronchoscopy detect tuberculosis?
Yes. Bronchoalveolar lavage is considered the gold standard for detecting any type of lung infection. For patients with pneumonia, we can determine exactly which pathogen is causing it.
What’s the one thing people should know about bronchoscopies?
Go to a place like MD Anderson which does a large number of complex bronchoscopies each year and has a lot of expertise in them. That level of experience will give you a better outcome.
MD Anderson is also at the forefront of using ablation therapy during bronchoscopy to treat small, peripheral lung cancers through clinical trials. We are the pioneers in this field, and only a handful of cancer centers offer it right now.
Roberto Casal, M.D., is an interventional pulmonologist specializing in bronchoscopies.
Request an appointment at MD Anderson online or call 1-877-632-6789.
Stage IV lung cancer survivor: Targeted therapy and surgery left me cancer-free
As a retired firefighter and combat veteran, I’ve been in some pretty tough situations. But the hardest thing I’ve ever done was sit my four children down and tell them I had stage IV lung cancer.
Two weeks earlier, they’d watched me lay one of my co-workers to rest after he’d died of stage IV pancreatic cancer. He was only 33. He was also a close family friend, so they had a front-row seat to his decline. They were worried I was next.
Fortunately, I chose MD Anderson for my lung cancer treatment. And in six months, I went from having tumors in my lungs, lymph nodes, ribs, and abdomen to showing no evidence of disease.
My lung cancer diagnosis
I was only 41 when I was diagnosed with lung cancer in September 2022. My first symptom was a dry cough that hung around after I recovered from a cold. My wife asked me repeatedly to get it checked out. When I finally did, the doctor thought it might be pneumonia and prescribed steroids and an antibiotic.
Nothing changed after a few weeks, so my doctor did some blood work. The tests kept coming back negative. Meanwhile, I was starting to feel worse. An X-ray revealed an area of concern in the lower lobe of my right lung, so my doctor sent me to a pulmonologist for a CT scan and a biopsy. Those results showed I had adenocarcinoma, a type of lung cancer.
MD Anderson has expertise in lung cancer with my specific genetic mutation
I initially sought treatment for lung cancer in Milwaukee. That’s the big city closest to my home in Wisconsin. But after getting a second opinion at MD Anderson, I decided to receive all of my care there.
With stage IV lung cancer, I already knew I was behind the eight ball. I was fighting for my life. So, once I found the best place in the nation for cancer care, it was hard to leave that and go anywhere else.
At MD Anderson, I met first with Dr. Carl Gay, a medical oncologist specializing in the treatment of thoracic cancers. He’s also an expert in a genetic mutation called anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusion, which my lung cancer had.
When I first found out about the mutation, I thought, “Great. Now, I’ve tested positive for something else.” But it turned out to be a blessing. Diseases with mutations often have more specific treatment options available than those that don’t. So, it was the best thing that could’ve happened to me. It meant we could use the genetic mutation against itself.
In the end, I found both the mutation and Dr. Gay’s expertise reassuring. Even though my doctors in Milwaukee were on the right track, none of their five thoracic medical oncologists were ALK specialists. And at MD Anderson at that time, 9 out of 15 were.
My lung cancer treatment
Dr. Gay and his colleagues reviewed my care plan after confirming my diagnosis. They all agreed: they wanted me to discontinue the chemotherapy that I’d started in Milwaukee and stay on an oral targeted therapy agent called alectinib instead. They’d seen some really good results with it and wanted to reserve chemotherapy as an option for later.
I took their advice. After only two months on that drug, the tumors in my lungs had shrunk by 50%. I could breathe a lot better. All of my lymph nodes were returning to normal size, too, and the area in my abdomen that had previously shown cancer activity did not light up on scans at all.
Surgery is not usually an option for patients with stage IV lung cancer. But MD Anderson has been a leader in offering surgery when appropriate, even with stage IV disease. And, they have enormous experience in performing operations on metastatic lung cancer. I did so well on the targeted therapy that surgery became an option for me. I jumped at the opportunity. It felt like my first chance to do something to strike back at the cancer, instead of just reacting to whatever it was doing.
Thoracic surgeon Dr. Mara Antonoff has a special interest in surgery for stage IV lung cancer and a lot of experience in performing it. She removed the middle and lower lobes of my right lung on March 24, 2023. I spent three days in the hospital and another week resting. When the pathology report came back, even my doctors were shocked. The cancer was completely gone. No living cancer cells could be found in any of the tissue samples taken from my lungs or lymph nodes. It was unbelievable.
Why I tell everyone to go to MD Anderson
In my mind, going from a stage IV lung cancer diagnosis to no evidence of disease is nothing short of a miracle. So, I feel blessed.
I had to take a medical retirement from firefighting, though, because the risks of smoke and chemical exposure were just too high for someone with my medical history and lung capacity. But I feel so good now that I’ve been savoring my time with family and friends. I’ve also been training again for an IRONMAN triathlon. I expect to compete in my second one of those on Sept. 8, in Madison.
That’s why I tell everyone to go to MD Anderson. With a stage IV diagnosis, I didn’t think I could ever be cancer-free, much less that fast. And I am so incredibly grateful.
Request an appointment at MD Anderson online or call 1-877-632-6789.
Lung anatomy & lung cancer spread
Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis
Early stage lung cancer often does not have symptoms. In addition, when symptoms appear they can easily be mistaken for common respiratory illnesses like bronchitis or pneumonia. Because of this, many cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Patients at high risk for lung cancer, especially those with a history of smoking, should undergo regular screenings in order to catch the disease at its early stages, when there is a better chance of cure.
If you have symptoms that signal lung cancer, your doctor will ask you questions about your medical, smoking and family history and whether you have been around certain chemicals or substances.
You will then undergo an imaging exam, typically a chest X-ray. Images cannot diagnose lung cancer, but they can show areas of concern. If the image shows such an area, the doctor may order other scans, including a CT scan or PET scan, for additional details regarding the area of concern.
If the findings on the imaging scans indicate cancer, the doctor will request that tissue or fluid be removed from the lung for examination. The act of obtaining a tissue or fluid sample is called a biopsy. There are several ways doctors can perform biopsies of lung tumors:
- Needle biopsy: A CT-guided biopsy where a needle is inserted through the skin under local anesthesia to acquire a tumor sample. One type of needle biopsy is fine needle aspiration (FNA), which uses a very small needle and suction to remove a small amount of tissue.
- Thoracentesis: Fluid from around the lungs is drawn out with a needle and tested for cancer cells.
- Bronchoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera is inserted through the nose or mouth and down into the lungs to obtain a small tissue sample (biopsy). This is usually performed under mild sedation. Bronchoscopies are rarely done alone. Bronchoscopy is usually performed with an endobronchial ultrasound.
- Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS): A bronchoscope with an attached ultrasound device is used to check for lung cancer inside nearby chest lymph nodes. EBUS is often performed at the same time as a bronchoscopy and requires general anesthesia.
- Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS): This minimally invasive surgical procedure uses a small camera to help retrieve tumor samples that are otherwise difficult to access. VATS requires a general anesthetic and is performed in the operating room by a thoracic surgeon.
- Thorascopy/pleuroscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera is inserted through a small incision in the back (for a thorascopy) or between the ribs (for a pleuroscopy). Doctors use this device to look for and retrieve suspected cancer tissue.
To complete assessment of how advanced the cancer is, which is called staging, the patient will undergo a PET-CT scan and an MRI or CT scan to check for signs of cancer spread to other organs, including the brain. This will guide the treatment decisions for each patient’s lung cancer.
In some cases, lung cancer can be passed down from one generation to the next. Genetic counseling may be right for you. Visit our family history site to learn more about genetic counseling and testing.
Treatment
At MD Anderson, some of the nation’s top lung specialists focus their extraordinary expertise on you. We customize your treatment to deliver the most advanced, effective and least invasive treatments available for lung cancer. And because your peace of mind is important to us, we specialize in techniques and therapies than can help preserve lung function and quality of life
We’re constantly researching safer and more effective treatments for lung cancer with fewer side effects. We are proud to be one of the few cancer centers in the nation to house a prestigious federally funded lung cancer SPORE (Specialized Program of Research Excellence) program. This leads to a large number of active clinical trials at MD Anderson and ensures that our patients have access to some of the most cutting-edge therapy anywhere in the world.
If you are diagnosed with lung cancer, your doctor will discuss the best options to treat it. This depends on several factors, including the stage and type of lung cancer; other lung problems, such as emphysema or chronic bronchitis; other prior or current medical conditions; and possible side effects of treatment.
Your treatment for lung cancer will be customized to your particular needs. It may include one or more of the following therapies to treat the cancer and help relieve symptoms.
Surgery
Surgery may be a good option for those with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. In some cases, patients may receive chemotherapy or radiation before surgery to shrink the tumor. This is called neoadjuvant therapy.
The most common types of surgery for lung cancer, in order of the amount of lung tissue removed, are:
- Wedge resection: Removal of the tumor and a pie- or wedge-shaped piece of the lung around the tumor. This procedure is typically used to perform a biopsy of a lung nodule.
- Segmentectomy or segmental resection: Removal of a segment, or part, of the lobe where the cancer is located. Both the segmentectomy and wedge resection are typically performed on patients who have limited lung capacity and can’t tolerate the removal of a larger section of the lung. They are also a good option for patients with small early-stage tumors generally measuring less than two centimeters. Both preserve lung capacity and the patient’s quality of life.
- Lobectomy: Removal of the lung lobe where the cancer is located. This is considered the “standard of care” for most lung cancer patients who undergo surgery.
- Sleeve lobectomy: A more complex form of lobectomy that is typically used for centrally located tumors. It involves removing the lobe where the tumor is located and part of the connecting bronchus. The cut bronchus is then connected with the remaining lobes. Though not always possible, sleeve lobectomies are preferable to pneumonectomy (complete removal of the lung) in order to preserve more functioning lung tissue.
- Pneumonectomy: Removal of an entire lung. This surgery is occasionally required due to the location of the tumor. In people with lungs that are otherwise healthy and function normally, pneumonectomy is well tolerated.
During most of these procedures, the surgeon will also remove lymph nodes from the chest. Since cancer often spreads through these nodes, doctors will examine them under a microscope to find out if the lung cancer has moved outside the lungs. This will help doctors decide if you need further treatment after surgery, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy or targeted therapy. Treatment following surgery is called adjuvant therapy.
Surgical approaches
For some lung cancer surgeries, there are different ways to perform the same procedure. Your surgeon will work with you to choose the best option. These methods include:
- Open surgery: The traditional surgical method. Surgeons perform the procedure through a four- to eight-inch incision between the ribs.
- Minimally invasive surgery: These procedures require several smaller incisions, typically between ¼ and ½ inch, and usually have a shorter recovery time and less pain for the patient. There are two primary methods of minimally invasive surgery for lung cancer patients.
- Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) or thoracoscopy: This technique uses a small camera and instruments that are inserted into the chest allowing the surgeon to perform the surgery through small incisions. It is typically performed on patients with small, early stage lung cancers.
- Robotic-assisted Surgery: This newer method of minimally invasive surgery uses robotic arms remotely controlled by the surgeon. Better images of the surgical site and greater instrument dexterity allow the surgeon to perform more complex surgery than is possible with VATS.
Statistically speaking, the more experienced the surgeon, the better the outcomes for lung cancer patients. MD Anderson’s Thoracic Center is home to many of the field’s most highly trained, experienced and respected thoracic surgeons. They operate only on cancers involving the chest and use the most advanced surgical techniques to treat a wide variety of lung cancers, including highly complex cases.
All patients with lung cancer who undergo surgery at the Thoracic Center enroll in a program of enhanced recovery, which aims to minimize pain, surgical stress and downtime. This leads to faster recovery, fewer side effects and better quality of life following surgery.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses focused, high-energy photon beams to destroy lung cancer cells. It is performed by a radiation oncologist, a specialist who is specially trained to treat cancer with ionizing radiation. At most hospitals, radiation oncologists are expected to treat several different types of cancer. MD Anderson’s Thoracic Center has radiation oncologists dedicated exclusively to caring for patients with lung cancer. This gives them incredibly deep experience in designing treatment plans.
Working with these radiation oncologists is a team of radiation therapy specialists, including dosimetrists and medical physicists. Together, this team of experts develops models for several different treatment types and determines which is best for each patient. This way, MD Anderson can deliver the maximum amount of radiation with the least damage to healthy cells. The radiation therapy treatments used for lung cancer patients include:
- 3D-conformal radiation therapy: Several radiation beams are given in the exact shape of the tumor. This is primarily used as a palliative treatment and not to cure the disease.
- Brachytherapy: Tiny radioactive seeds are placed in the body close to the tumor. Brachytherapy is primarily used to treat metastatic growths in the airway. Since most of these growths can be treated with external beam radiation, brachytherapy is rarely used on lung cancer patients.
- Intensity-modulate radiotherapy (IMRT): Treatment is tailored to the specific shape of the tumor. This type of radiation is commonly used to treat cancers that have invaded nearby lymph nodes.
- Volumetric-modulate Arc therapy (VMAT): This is a special type of IMRT. In it, the part of the machine that shoots out the beam of radiation rotates around the patient in an arc. This can irradiate the tumor more precisely and shorten procedure times.
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): High doses of radiation delivered with several beams at various intensities and angles to precisely target the tumor. Learn more about SBRT.
Proton therapy
A type of radiation therapy, proton therapy delivers a high dose of radiation directly to the tumor, sparing nearby healthy tissue and organs. MD Anderson operates one of the world’s largest and most advanced proton therapy centers. Read more about proton therapy and how it is used to treat lung cancer.
Systemic Therapy
Systemic therapy is an umbrella term for treatments that use substances that travel through the bloodstream to reach affected cells all over the body. There have been significant advances in systemic therapy treatments for lung cancer over the last decades. The medical oncologists at MD Anderson’s Thoracic Center are world-renowned in the care of lung cancer patients and have participated in the clinical trials that have led to the development of important new treatments, including targeted and immune therapies.
Targeted therapy
Cancer cells use specific molecules (often in the form of proteins) to survive, multiply and spread. Targeted therapies stop or slow the growth of cancer by interfering with, or targeting, these molecules. Currently there are targeted therapies for many subtypes of adenocarcinoma. Read more about targeted therapies.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapies recruit the body’s own immune system in the fight against cancer. The current standard of care for non-small cell lung cancer includes the use of checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapies, which take the natural “brakes” off the immune system, allowing it to attack cancer cells. This treatment can lead to durable responses and has revolutionized care for lung cancer patients. Read more about immunotherapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to directly kill cancer cells by stopping their growth. This form of treatment is commonly combined with immunotherapy. In combination, both drugs become more effective. Learn more about chemotherapy.
Angiogenesis inhibitors
Angiogenesis is the process of creating new blood vessels. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the main molecules that control the process. Some cancerous tumors are very efficient at using these molecules to create new blood vessels, which increases blood supply to the tumor and allows it to grow more rapidly.
Researchers developed drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors, or anti-angiogenic therapy, to disrupt the growth process. These drugs search out and bind themselves to VEGF molecules or receptor proteins, prohibiting them from activating angiogenesis.
Learn more about lung cancer:
In some cases, lung cancer can be passed down from one generation to the next. Genetic counseling may be right for you. Visit our family history site to learn more about genetic counseling and testing.
Frequently asked questions
What is small cell lung cancer?
Lung cancer is traditionally categorized by the type of cell where it begins. Small cell lung cancers (SCLCs) make up about 15% of lung cancers and almost always are caused by smoking tobacco. The cancer often starts in the more central portions of the chest — in the bronchi, the two large tubes that carry air from the windpipe to the lungs. It usually grows and spreads quickly to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes. Because this cancer is so aggressive, surgery is used less often for SCLC than for non-small cell lung cancers.
What are the stages of lung cancer?
Lung cancer stages are determined through various tests and procedures, including MRIs, CT scans, PET scans, and lymph node biopsies. The doctor will combine the results of these procedures to stage the cancer, using the TNM (tumor, node, metastasis) classification system.
Can you get lung cancer from smoking?
Yes, you can get lung cancer from smoking. MD Anderson recommends lung cancer screening if you’re age 50–80, are a current smoker (or a former smoker who quit within the past 15 years), and have a 20 pack-year smoking history (for example, one pack a day for 20 years or two packs a day for 10 years).
Is lung cancer hereditary?
Lung cancer is hereditary in some cases, and a family history of lung cancer is considered a risk factor. Some rare genetic conditions, such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS), are associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer.
Is lung cancer curable?
Lung cancer is sometimes curable; it depends on the specific cancer a person has and how early the cancer was caught. Some lung cancers are very aggressive, while others are very responsive to targeted therapy and are curable if caught early.
How are CT scans used to diagnose lung cancer?
CT scans are used in certain instances, in combination with other tests, to help diagnose lung cancer. In the process of diagnosis, patients will typically undergo an imaging exam, usually a chest X-ray. Images alone are not enough to make a lung cancer diagnosis, but they can show areas of concern. If an image shows such an area, the doctor may order other scans, including a CT scan or a PET scan, to get additional details. If the findings of the image scans indicate cancer, the doctor will request the removal of tissue or fluid from the lung for examination. Obtaining a tissue or fluid sample is called a biopsy.
When is immunotherapy used to treat lung cancer?
Immunotherapy may be used in combination with chemotherapy as a treatment for lung cancer. However, its usefulness depends on the type of cancer being treated.
Why choose MD Anderson for your lung cancer treatment?
Choosing the right hospital may be the most important decision you can make as a lung cancer patient. At MD Anderson you’ll get treatment from one of the nation’s top-ranked cancer centers. Our expertise starts with the ability to accurately diagnose and stage even extremely rare cancers, then carries on through groundbreaking treatment and into survivorship.
As a patient at MD Anderson, you’ll see the benefits of care from a top-ranked cancer center. These include:
- Treatment from specialists who focus exclusively on lung cancer and other thoracic cancers, including radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, surgeons and pathologists.
- Molecular diagnosis of cancer cells, allowing doctors to identify which treatments have the best chance of success against your exact cancer.
- Expert surgical care designed to offer complete resection of your tumor and any involved lymph nodes.
- An enhanced surgical recovery program along with robotic and minimally invasive procedures that offer faster recovery times and less pain from surgery.
- Groundbreaking clinical trials that may not be available anywhere else. These include trials of new targeted therapies, immunotherapies and drug combinations.
MD Anderson patients also have access to all the services and support offered by one of the nation’s top-ranked comprehensive cancer centers. From counseling and support groups to integrative medicine and physical therapy, MD Anderson has all the support and wellness services needed to treat the whole person – not just the disease.
This support and care is available beyond MD Anderson’s campus in the Texas Medical Center. Through our Houston-area locations, patients throughout the region can get top-ranked care and personalized attention close to home.
They're focused on you as a person, and they're focused on fighting the disease. But they also show so much kindness and compassion.
Alexa DiVenere
Survivor
Treatment at MD Anderson
MD Anderson lung cancer patients can get treatment at the following locations.
Featured Articles

Neoplasms 101: What they are and how they’re treated

Stage IV lung cancer survivor: Why you should start your treatment at MD Anderson

Advances in small cell lung cancer classification

MD Anderson helps survivor through three cancer diagnoses

Lung cancer survivor grateful for immunotherapy clinical trial

Stage IV lung cancer survivor: Targeted therapy and surgery left me cancer-free

Does vaping cause lung cancer?

Four-time cancer survivor: Why I’m glad I went to MD Anderson
Clinical Trials
MD Anderson patients have access to clinical trials offering promising new treatments that cannot be
found anywhere else.
Becoming Our Patient
Get information on patient appointments, insurance and billing, and directions to and around MD Anderson.
myCancerConnection
Talk to someone who shares your cancer diagnosis and be matched with a survivor.
Prevention & Screening
Many cancers can be prevented with lifestyle changes and regular screening.
Counseling
MD Anderson has licensed social workers to help patients and their loved ones cope with cancer.
Help #EndCancer
Give Now
Donate Blood
Our patients depend on blood and platelet donations.
Shop MD Anderson
Show your support for our mission through branded merchandise.